The No-Code EDI Revolution: How Supply Chain Teams Are Solving the Critical Skills Shortage While Cutting Implementation Time by 90%
The EDI professional shortage has reached crisis levels. 29% of businesses say that they lack the skilled resources to build and manage integrations between systems, applications, and partner ecosystems, while many of the professionals who initially implemented and managed EDI systems are now reaching retirement age, taking with them years of specialized knowledge and hands-on experience. Supply chain teams can't wait months for custom integrations anymore.
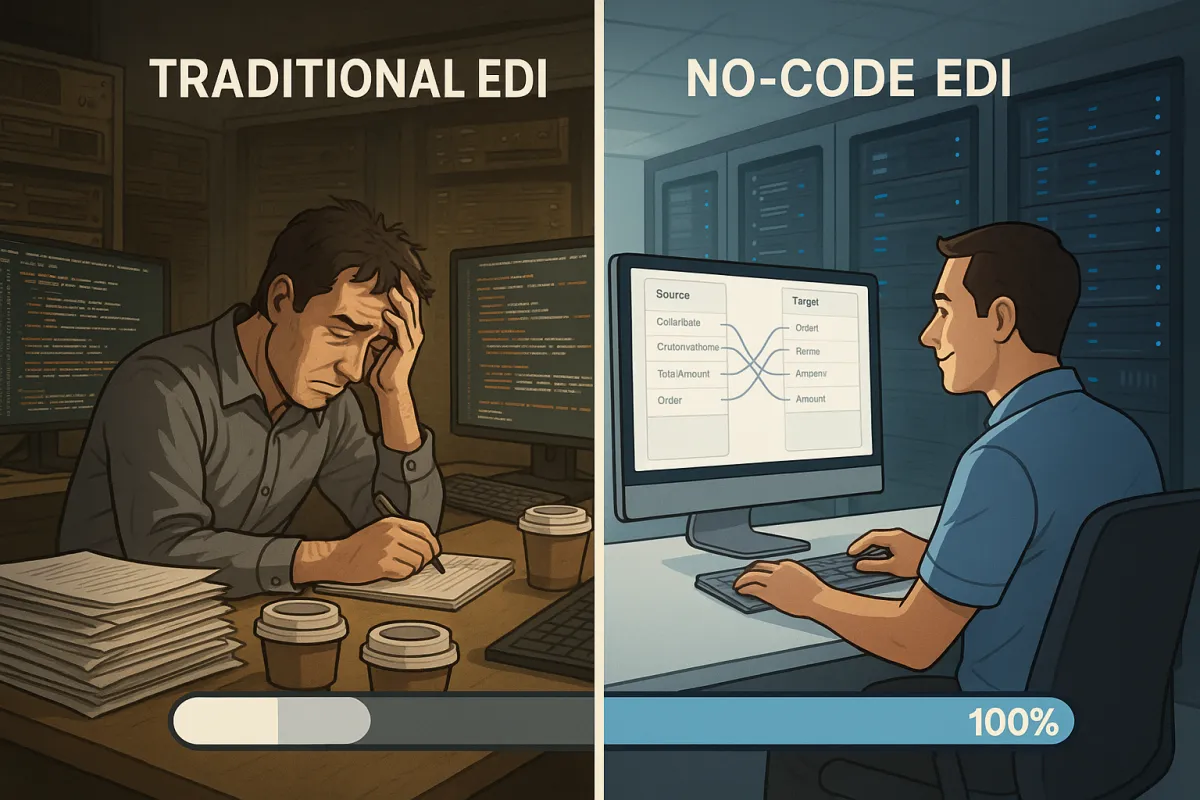
That's where no-code EDI implementation platforms are changing everything. Organizations report up to 90% reduction in development time. Companies implementing no-code platforms achieve up to 90% reduction in development time, transforming project timelines from months to weeks or even days. Projects that used to take 6-8 months now complete in 3-4 weeks.
The EDI Skills Crisis Threatening Supply Chain Operations
The numbers paint a stark picture. A lack of cloud skills cost businesses up to $258 million annually, according to the London School of Economics. The situation gets worse when you look at broader IT trends: IDC predicts that by 2026, more than 90% of organizations worldwide will feel the pain of the IT skills crisis, amounting to some $5.5 trillion in losses caused by product delays, impaired competitiveness, and loss of business.
EDI faces a double problem. Not only are experienced professionals retiring, but many universities and technical schools offer degrees in information technology, computer science, and business management, EDI is rarely a focus of these programs. The specialized nature of EDI, along with the reliance on standards like ANSI X12 and EDIFACT, requires specific technical training that is often not covered in general IT education.
The result? Companies scramble to maintain critical B2B connections while their institutional knowledge walks out the door. The lack of effective knowledge transfer within organizations exacerbates the problem, as new hires often face a steep learning curve when it comes to understanding legacy systems and the complexities of EDI implementation and integration.
Why Traditional EDI Implementation Requires Specialized Expertise
Traditional EDI isn't just complex—it's arcane. Each implementation requires deep understanding of message standards, mapping protocols, and integration patterns that can take years to master. Most companies rely on homegrown solutions that only one or two people truly understand.
Consider a typical ANSI X12 850 purchase order implementation. You need to understand segment hierarchies, data element requirements, trading partner variations, and ERP integration points. Then multiply that across dozens of transaction sets and trading partners. It's no wonder most EDI professionals learn on the job, picking up knowledge as they go, which makes it difficult to scale expertise across the industry.
The No-Code Solution: Democratizing EDI Implementation
No-code EDI platforms flip the traditional model. Instead of requiring specialized knowledge, these platforms provide visual mapping tools, pre-built connectors, and automated validation. With EDI, you can use low-code environments to easily automate common file processing and sharing steps, saving time and effort.
The transformation is dramatic. Low code/ no-code platforms have the potential to reduce the development time by 90%, while 71% of organizations that leverage citizen development has sped up application development by at least 50% and 29% of companies have seen a 2X or more jump in delivery time.
Here's what makes the difference: these platforms handle the technical complexity behind intuitive interfaces. Drag-and-drop mapping replaces manual coding. Pre-validated templates eliminate syntax errors. Automated testing catches integration issues before they hit production.
Leading platforms like Cleo, Jitterbit, and Cargoson are incorporating no-code capabilities that let business users configure EDI connections without deep technical knowledge. The focus shifts from "how to code this mapping" to "what business rules need to be implemented."
Key Features That Make EDI Accessible to Business Users
Modern no-code EDI platforms include several features that eliminate traditional barriers:
Pre-built connectors handle the heavy lifting for common ERP systems, cloud platforms, and trading partner networks. These aren't just basic templates—they're production-ready integrations that understand the nuances of different systems.
Visual mapping tools replace code-based transformation logic. Users can see source and target structures side by side, creating mappings through point-and-click interfaces. Complex business rules get configured through dropdown menus and form fields instead of custom scripts.
Automated validation occurs in real-time. The platform checks data formats, required fields, and business rules as users configure mappings. This prevents the trial-and-error cycles that plague traditional implementations.
Self-service partner onboarding becomes possible when non-technical users can configure new trading partner connections using guided workflows. What used to require weeks of technical work now takes hours of business configuration.
Quantifying the Business Impact
The financial benefits are substantial. Organizations save average of $187,000 annually with no-code platforms. Survey data reveals companies achieve $187,000 per year in savings, with variation by size and use case complexity.
But the real value lies in speed and resource optimization. Citizen developers cost 40–60% less than professional developers. Enabling business users reduces development costs by 40–60% compared to hiring professional programmers. For EDI specifically, this means supply chain teams can handle their own integrations instead of waiting for scarce technical resources.
The time savings compound over multiple projects. The average company avoided hiring two IT developers using low code tools, while this reaped about $4.4 million in increased business value over three years from the applications designed.
Speed-to-Market Advantages
Traditional EDI projects follow predictable timelines: 2-3 months for requirements gathering, 3-4 months for development and testing, 1-2 months for trading partner testing. No-code platforms compress this to weeks.
Partner onboarding accelerates dramatically. New trading partners can be connected in days instead of months. This agility becomes crucial when you're responding to supply chain disruptions or onboarding new suppliers quickly.
The reduced IT dependency matters more than cost savings for many organizations. Supply chain teams can respond to changing business requirements without submitting IT tickets and waiting in development queues.
Implementation Strategy: Moving from Traditional to No-Code EDI
Successful migration requires careful planning. Start by assessing current EDI complexity—not all scenarios fit no-code approaches immediately. High-volume, complex transformations might need hybrid solutions combining no-code configuration with traditional development where necessary.
Training becomes critical for success. 70% of low code users who had no experience at all before using low code platforms learned low code in 1 month or less. The key is identifying the right business users—those who understand EDI requirements but aren't necessarily technical.
Transport management system providers like Cargoson, nShift, and BluJay are building no-code EDI capabilities directly into their platforms. This integration approach eliminates separate tools and provides context-aware configuration options.
Change management matters as much as technology. Investing in internal training programs and mentorship opportunities can help companies build a pipeline of EDI talent from within their own workforce. By pairing new hires with experienced professionals, organizations ensure valuable institutional knowledge is passed on.
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
Data quality concerns top the list of objections. Business users worry about creating mappings without understanding all the technical implications. Modern platforms address this through built-in validation, testing environments, and approval workflows that let technical users review configurations before production deployment.
Security and compliance require careful attention. While no-code platforms simplify configuration, they must maintain the same security standards as traditional implementations. Look for platforms that provide audit trails, role-based access controls, and compliance certifications relevant to your industry.
Integration with existing systems needs planning. No-code platforms excel at standard integrations but may struggle with highly customized legacy systems. Hybrid approaches work well—use no-code for standard scenarios while maintaining traditional development for edge cases.
The Future of Democratized EDI
The convergence of AI and no-code platforms promises even greater accessibility. AI integration transforms platforms into intelligent assistants. AI is transforming platforms from visual builders into intelligent systems that interpret requirements and generate solutions.
EDI becomes a foundational enabler for enterprise automation and AI initiatives. Gartner forecasts that by 2029, enterprise low-code application platforms will power 80% of mission-critical applications globally, a dramatic leap from just 15% in 2024.
The hybrid model gains traction as organizations realize different scenarios need different approaches. Hybrid models combine no-code with traditional coding to balance accessibility with capability.
Transport management platforms from Manhattan Active, Blue Yonder, and Cargoson are evolving to support these hybrid approaches, providing no-code configuration for standard scenarios while maintaining API access for custom requirements.
Building Tomorrow's EDI-Capable Workforce
The citizen developer movement reshapes EDI skills requirements. 83% of tech leaders have implemented a Citizen Development program, with 92% agreeing that it plays a vital role in achieving their digital transformation objectives.
Organizations need new training approaches that focus on business process understanding rather than technical implementation details. Gartner predicts active citizen developers will be at least 4X the number of professional developers' at large enterprises.
Academic institutions are beginning to recognize this shift. Collaborations between businesses and academic institutions can create specialized EDI training courses or certifications as part of broader IT or supply chain management programs. These initiatives help equip the next generation with the skills needed to manage and evolve EDI systems.
The future workforce combines business domain expertise with platform configuration skills. Instead of training people to code EDI mappings, we're training them to understand business requirements and configure platforms to meet those needs.
This shift from "EDI developer" to "EDI configurator" opens career paths for supply chain professionals who understand the business context but may lack traditional programming skills. It's a fundamental change that makes EDI expertise more accessible while maintaining the business knowledge that makes implementations successful.
The no-code EDI revolution isn't just about technology—it's about making critical business capabilities accessible to the people who understand them best. When supply chain teams can configure their own integrations, respond to changing requirements quickly, and onboard partners without technical bottlenecks, the entire organization becomes more agile and responsive.