The 7 Critical EDI-Blockchain Integration Barriers That Doom 73% of Pilot Projects: Your Complete Implementation Framework to Overcome Technical, Cost, and Vendor Challenges in 2025
Most companies diving into EDI blockchain integration expect enhanced security, real-time transaction visibility, and improved traceability of documents, yet investment in blockchain is almost doubling year on year and is expected to exceed £7.5 billion by next year. Despite this massive investment, most pilot projects hit the same seven barriers that have been sinking EDI-blockchain initiatives since companies started experimenting with this technology combination.
The promise looks compelling on paper. IDC research suggesting businesses will gain a 308% ROI with modernised B2B integration, and blockchain advocates talk about tamper-proof records and eliminated intermediaries. But here's what actually happens when you try to merge these technologies at enterprise scale.
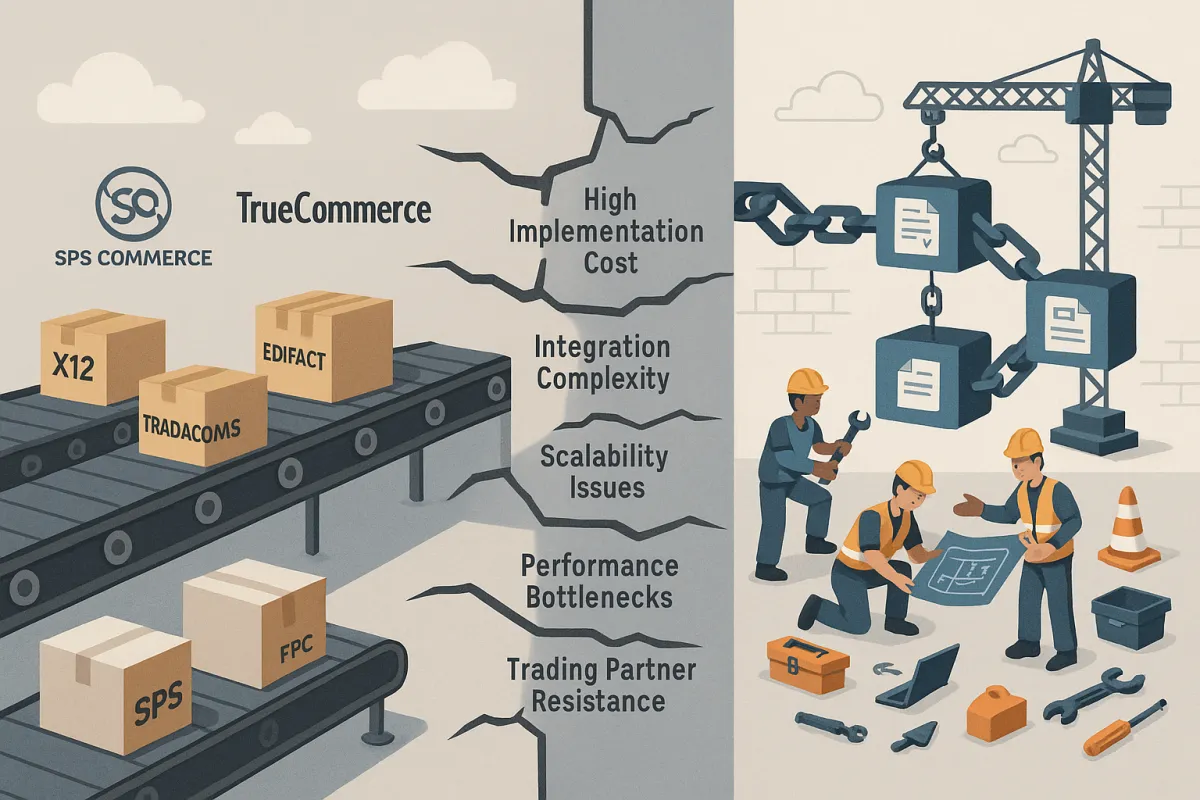
Barrier #1: The $120,000 Implementation Cost Crisis
Initial implementation costs for blockchain can be higher due to the need for specialized technology and expertise. While pilot programs might start around $15,000 for proof-of-concept testing, full enterprise implementations routinely exceed $120,000 before you've processed your first production transaction.
The often high costs associated with EDI implementation and maintenance can be prohibitive, especially for smaller businesses. This is because Blockchain requires a lot of computing power—leading to higher energy consumption and escalated power costs. You're not just paying for software licenses here. The real costs hit when you discover your existing EDI infrastructure needs substantial modifications, your staff requires months of training, and you need dedicated blockchain architects who command premium salaries.
Compare this to proven TMS solutions like MercuryGate, Oracle Transportation Management, or Cargoson, where implementation costs remain predictable and ROI timelines are well-established. Traditional EDI providers like SPS Commerce and TrueCommerce offer clear pricing models that don't require you to bet the company's integration budget on experimental technology.
Barrier #2: The Integration Complexity Trap
Technically, blockchain requires expertise, infrastructure, and standards to implement and maintain—therefore, you may need to invest in training and development. Your current ERP systems weren't designed to talk to blockchain networks, and bridging that gap means building custom middleware that becomes a maintenance nightmare.
Most EDI systems already struggle with data mapping between different standards. Add blockchain's immutable ledger requirements, and you create integration complexity that even experienced system integrators find challenging. There are multiple EDI standards in use like TRADACOMS, GS1, X12. They have been around for more than 3 decades, thus lot of legacy infrastructure exists with an enterprise. Thus till the enterprise fully transform (which may take another decade), EDI has to be integrated with Blockchain technology.
Smart transportation management platforms like Transporeon, nShift, and Cargoson have spent years simplifying integration challenges with pre-built connectors and standardized APIs. When you're dealing with hundreds of trading partners, proven integration approaches beat experimental blockchain architectures every time.
Barrier #3: Scalability and Performance Bottlenecks
Blockchain networks can sometimes be slow or inefficient while validating transactions. This is because Blockchain requires a lot of computing power—leading to higher energy consumption and escalated power costs. Your peak EDI transaction volumes during month-end close periods will overwhelm most blockchain networks.
Traditional EDI processes thousands of transactions per minute during busy periods. Blockchain networks, even enterprise-grade ones, struggle with transaction throughput that modern supply chains demand. The consensus mechanisms that make blockchain secure also make them slower than the point-to-point connections your business relies on.
Established TMS platforms like Blue Yonder, Manhattan Active, and Cargoson handle massive transaction volumes without the performance penalties that blockchain consensus protocols introduce. When your business depends on real-time shipment updates and instant invoice processing, blockchain's theoretical benefits don't compensate for practical performance issues.
Barrier #4: Trading Partner Resistance and Adoption Challenges
Your blockchain implementation might be technically perfect, but it fails if your trading partners won't participate. As-a-service models are changing EDI from a tool that costs a lot of money to a service that you can pay for as you go. EDIaaS suppliers offer managed services that make IT work easier and help businesses quickly enroll partners and stay in line with trading regulations.
Small suppliers especially resist adopting new technology when their current EDI setup works fine. They see blockchain requirements as additional cost and complexity without clear benefits. Large retailers might mandate EDI compliance, but they can't force suppliers to adopt experimental blockchain networks.
Successful shipping platforms like ShippyPro, Sendcloud, and Cargoson overcome adoption barriers by offering multiple integration options and gradual migration paths. They understand that ecosystem success depends on making technology adoption easier, not harder, for trading partners.
Barrier #5: Security and Compliance Paradoxes
The same cannot be said for Blockchain. Depending on the industry and region, Blockchain technology may be subject to evolving regulatory frameworks. There could be regulatory uncertainty regarding data governance, taxation, and liability when using blockchain because many governments and regulators are still figuring out whether certain laws should be updated to properly address Blockchain decentralization.
Blockchain's immutable ledger conflicts with GDPR's "right to be forgotten" requirements. You can't delete personal data from a blockchain without compromising the entire network's integrity. This creates compliance nightmares for companies handling European customer data.
Meanwhile, Cargoson and other established platforms build compliance features directly into their architecture. They handle data residency requirements, audit trails, and regulatory reporting without forcing you to navigate blockchain's regulatory uncertainty.
Barrier #6: Technical Expertise and Skills Shortage
Using blockchain for EDI comes with some challenges to consider, such as technical complexity, regulatory uncertainty, cultural resistance, and scalability issues. Technically, blockchain requires expertise, infrastructure, and standards to implement and maintain; thus, you may need to invest in training and development.
The shortage of qualified blockchain developers intersects with the already limited pool of EDI specialists. You need people who understand both legacy EDIFACT standards and modern blockchain architectures. These professionals command salaries that make implementation costs even higher.
Traditional TMS providers like Oracle TM, SAP Transportation Management, and Cargoson offer comprehensive training programs and certified implementation partners. You don't need to hunt for rare blockchain-EDI specialists when proven platforms come with established support ecosystems.
Barrier #7: Vendor Lock-in and Platform Selection Risks
There are multiple approaches being adopted, the two successful ones are EEA (Enterprise Ethereum Alliance) who use permissioned Ethereum blockchain (Besu & Quorum) and Baseline uses public Ethereum network in conjunction with ZKP (Zero Knowledge Proofs). Choosing the wrong blockchain platform creates vendor lock-in that's harder to escape than traditional EDI arrangements.
Each blockchain platform has incompatible architecture and different smart contract languages. Migration between platforms means rebuilding your entire integration layer, not just switching data formats. This creates strategic risk that most IT directors find unacceptable.
When evaluating solutions, consider how providers like IBM Sterling, Cleo, and Cargoson offer flexibility through standard protocols and open APIs. Avoid experimental blockchain platforms that force architectural decisions you might regret in three years.
Your 2025 Implementation Success Framework
Start with proven hybrid approaches that deliver blockchain benefits without the integration complexity. Start with a pilot program to test the blockchain integration on a smaller scale. Assess current EDI: Evaluate your current EDI setup and identify areas that could benefit from blockchain integration. Develop a pilot: Start with a pilot program to test the blockchain integration on a smaller scale.
Focus on specific use cases where blockchain adds genuine value. Supply chain traceability for pharmaceuticals or high-value goods justifies implementation complexity better than routine invoice processing. This level of transparency is especially critical in industries where traceability, compliance, and data integrity are paramount. Key use cases for EDI blockchain applications include: Automating the validation of certificates, such as proofs of origin.
Consider platforms that integrate blockchain capabilities without requiring complete EDI replacement. Blockchain will not replace or supplant EDI, but in some cases will form the basis for new and optimized EDI processes. As a result, blockchain will probably be more of a complementary technology to "traditional" EDI and at the same time an enabler of further potentials and use cases in supply and value chains and beyond.
Establish clear success metrics beyond theoretical blockchain benefits. Measure actual transaction costs, integration time, and trading partner adoption rates. Partner with experienced providers like Cargoson who understand both traditional EDI requirements and emerging technology capabilities.
Remember that blockchain will likely eventually augment or extend the capabilities of EDI rather than displace or replace this entrenched, reliable, efficient, and standardized mainstay of ecosystem integration. And by the way, I still haven't found a more productive way to exchange a purchase order than EDI. Your 2025 strategy should enhance proven systems rather than replace them with experimental alternatives.