The Complete EDI Alert Notification System Implementation Guide: How to Build Proactive Monitoring That Prevents Supply Chain Disruptions Before They Escalate in 2025
Most legacy EDI systems leave you in the dark when something goes wrong. A file fails, but you're not told why, or worse, you find out after your customer does. This reactive approach costs companies millions in missed orders, delayed shipments, and damaged trading partner relationships. 85% of businesses utilize EDI for B2B transactions, yet over 80% of data integration projects either fail or exceed their original budget by more than 170%.
The solution? Building comprehensive EDI alert notification systems that catch problems before they escalate. 88% of reviewers rated real-time alerts as important or highly important for providing immediate insights into transaction statuses, yet many organizations still rely on manual monitoring or discover issues only after partners complain.
The Hidden Cost of Reactive EDI Management
There's no intuitive dashboard to track status, no alerting system to flag issues in real time, and no way to pinpoint whether the failure happened during mapping, routing, or partner communication. This visibility gap forces IT teams into constant firefighting mode.
Consider the cascading effects: Lost or failed EDI transactions can lead to operational inefficiencies, such as missed orders, delayed shipments, or inventory discrepancies. Delays or failures in transmitting or receiving EDI documents can cause significant disruptions in the supply chain, leading to procurement delays, missed deliveries, and potential financial penalties.
The financial impact extends beyond immediate penalties. The cost of EDI errors extends beyond immediate financial penalties to include operational inefficiencies, employee burnout, and damaged business relationships. When your ASN fails to transmit and a major retailer's shipment sits in limbo, you're looking at chargebacks, expedited shipping costs, and strained partnerships that take months to repair.
Organizations running legacy platforms from traditional providers often discover issues only when trading partners escalate problems. By then, damage control becomes exponentially more expensive than prevention.
Essential Components of an Effective EDI Alert System
Effective EDI monitoring requires four core components working in harmony. First, real-time transaction tracking that captures every message state from initiation to acknowledgment. Real-time updates on the status of individual EDI transactions enable stakeholders to track the progress of critical documents and proactively find potential delays.
Second, intelligent error detection that goes beyond simple transmission failures. Your system needs to validate data integrity, check for missing mandatory fields, and identify unusual transaction patterns. Patterns of repeated transmission or acknowledgment errors might indicate a systemic issue.
Third, comprehensive logging and reporting capabilities. Businesses can utilize detailed logs and error codes to identify the root cause of transaction failures and resolve issues promptly. Without detailed audit trails, troubleshooting becomes guesswork.
Fourth, flexible notification systems that adapt to your organizational structure. Real-time notifications and alerts via email and SMS for a failed transaction, missing acknowledgement, or processing delayed beyond defined thresholds. Different stakeholders need different information at different times.
Modern TMS platforms like Cargoson, MercuryGate, and Descartes increasingly incorporate these monitoring capabilities directly into their core offerings, recognizing that transportation visibility depends on reliable EDI data flows.
Critical Alert Categories for Supply Chain Operations
Your alert system should prioritize five critical scenarios. Transaction failures demand immediate attention - when EDI 850 purchase orders fail to process, production planning stops. Acknowledgment delays signal communication breakdowns; if 997 functional acknowledgments don't arrive within expected timeframes, you can't confirm successful delivery.
Certificate expiration alerts prevent AS2 communication failures. Many organizations discover expired certificates only when partners can no longer receive secure transmissions, disrupting entire supply chains overnight.
Volume anomalies often indicate deeper issues. During routine monitoring, they identified an unexpected spike in document volume for a specific customer. Upon further investigation, they discovered that an ERP system issue was causing a document to loop repeatedly.
Partner-specific alerts help maintain relationship health. When a key supplier's EDI patterns change - fewer advance ship notices, delayed invoices, or format inconsistencies - early warnings enable proactive communication rather than reactive damage control.
Building Your EDI Alert Architecture
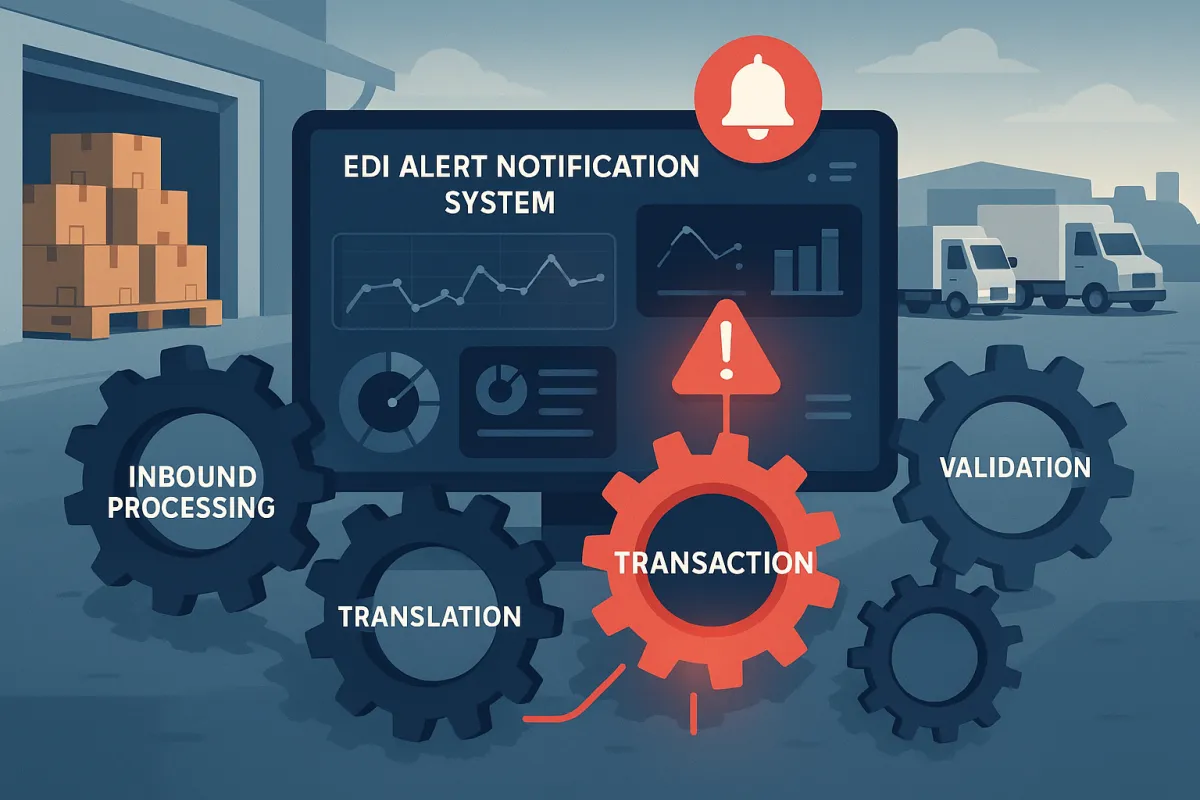
Start with data collection infrastructure that captures transaction metadata in real-time. Your monitoring system needs hooks into every stage of the EDI pipeline: inbound processing, translation, validation, routing, and outbound delivery. Searching for events with sourcetype="edi:x12" will retrieve all EDI transactions, including both the actual transactions and their corresponding acknowledgments.
Integration with platforms like Splunk enables advanced analytics and pattern recognition. Splunk ITSI for further expanding the analytics, leverage the ITSI thresholding and anomaly detection capability. This combination allows you to detect subtle patterns that manual monitoring would miss.
Design your alert infrastructure with configurable thresholds and escalation paths. A missing acknowledgment might trigger an informational alert after 30 minutes, a warning after two hours, and a critical alert with SMS notifications after four hours. Different document types require different urgency levels.
Consider hybrid architectures that combine on-premises monitoring with cloud-based analytics. Organizations using TMS solutions like Cargoson often benefit from centralized monitoring that spans multiple transportation providers and EDI endpoints, providing unified visibility across complex supply networks.
Dashboard Design and User Experience Optimization
An EDI Dashboard acts like a command centre, providing instant visibility and control over your EDI transactions and processes. However, effective dashboards require careful design tailored to different user roles and responsibilities.
IT administrators need technical details: transmission rates, error codes, system performance metrics, and integration health. Supply chain managers require business-focused views: order processing status, shipment delays, partner performance metrics, and compliance indicators.
Designing a user-friendly interface for all users to navigate and access information quickly. A user-friendly interface should feature clear menus, intuitive navigation, and customized dashboards. Avoid information overload by providing role-based filtering and customizable widgets.
Employ various data visualisation techniques, such as charts, graphs, and tables. This helps you understand the trends, patterns, and anomalies clearly. Heat maps showing partner performance, time-series charts displaying transaction volumes, and geographic visualizations for shipment tracking all provide different insights.
Modern TMS platforms incorporate these dashboard principles, recognizing that logistics visibility requires intuitive interfaces that non-technical stakeholders can use effectively. Solutions from providers like Cargoson, Manhattan Associates, and Oracle WMS demonstrate how transportation management benefits from EDI monitoring integration.
Advanced Alert Configuration and Automation
Intelligent alerting goes beyond simple threshold-based notifications. Implement conditional logic that considers context: is this partner historically reliable? Does this error pattern coincide with known maintenance windows? Are similar issues affecting multiple partners simultaneously?
We applied ECGrid Simplify's data validation rules to automatically verify that all required information was present before Advanced Shipping Notices (ASNs) were transmitted to trading partners. When key data was missing, the platform enabled the customer to manually input the necessary details, ensuring ASNs could still be sent on time. This proactive approach helped customers maintain EDI compliance and avoid costly delays during their ERP migration.
Automated partner communication reduces manual intervention. When missing acknowledgments are detected, your system can automatically send follow-up inquiries through established communication channels. If certificate expiration approaches, automated notifications to both internal teams and affected partners ensure timely renewal.
Data validation rules should operate at multiple levels. Pre-transmission validation catches formatting errors before they leave your system. Post-processing validation ensures received data meets business rules. Real-time validation during mapping identifies transformation issues immediately.
Integration with modern TMS platforms requires special consideration for transportation-specific scenarios. Cargoson and similar solutions need alerts for carrier capacity changes, route optimization impacts, and shipping deadline conflicts that affect EDI document timing.
Implementation Roadmap and Success Metrics
Begin implementation with a phased approach focusing on your highest-value trading partners and most critical document types. Start with basic transaction monitoring for EDI 850, 855, 856, and 810 documents - the core purchase order lifecycle that drives most supply chain operations.
Phase two adds advanced analytics and predictive alerting. By setting up real-time alerts and dashboards, you can maintain visibility into the health of your supply chain and act on issues as soon as they arise. This phase should include integration with existing monitoring tools and ITSM platforms.
Phase three implements automated response workflows and partner-specific customizations. Different trading partners have different tolerances for error rates, acknowledgment timing, and communication preferences.
Measure success through key performance indicators: mean time to detection (MTTD) for EDI issues, reduction in partner-reported problems, decreased manual monitoring effort, and improved transaction success rates. These KPIs can also help identify potential infrastructure issues that might hinder your organization's ability to process critical EDI information across your supply chain partners.
For organizations implementing modern TMS solutions, EDI alert systems become force multipliers. Platforms like Cargoson benefit from proactive monitoring that ensures transportation visibility isn't compromised by data communication failures. When shipment tracking depends on reliable ASN processing, monitoring systems prevent visibility gaps that could cascade through entire logistics networks.
The investment in comprehensive EDI alert systems pays dividends through reduced operational disruptions, improved partner relationships, and enhanced supply chain resilience. Real-time monitoring capabilities enable businesses to identify issues as they arise, reducing the risk of errors cascading through the system and causing operational disruptions.